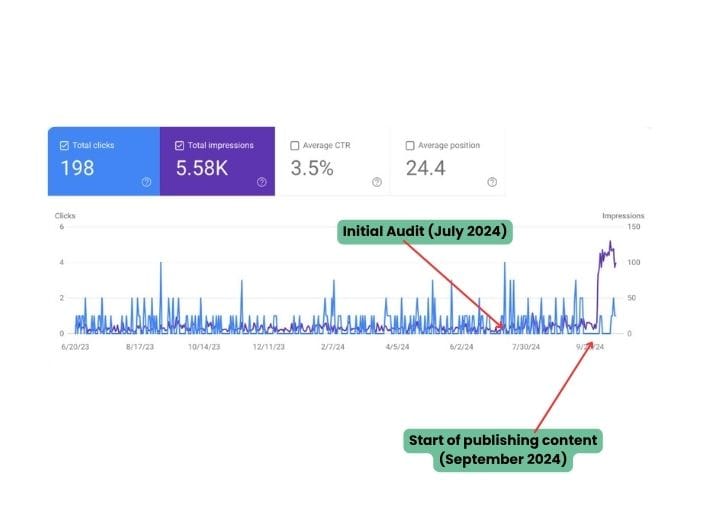
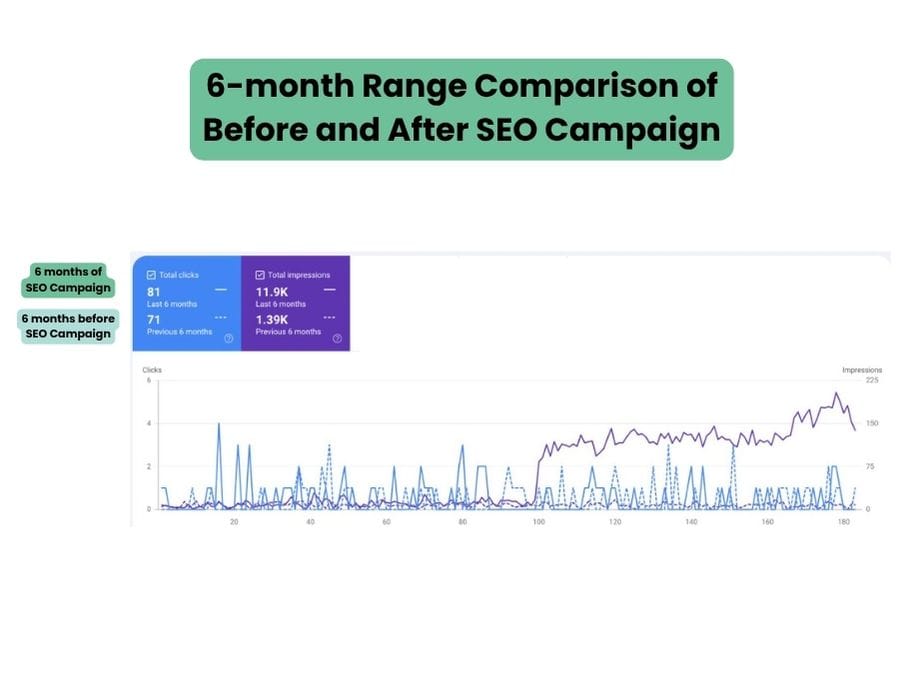
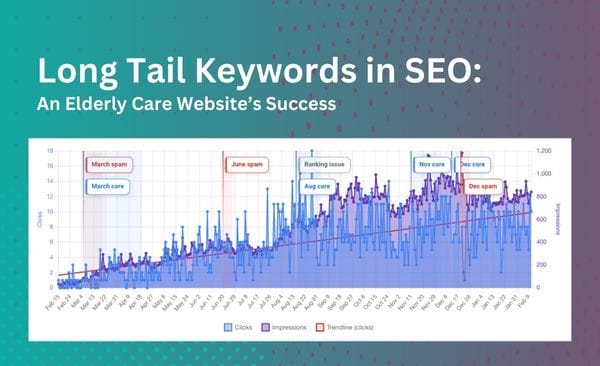
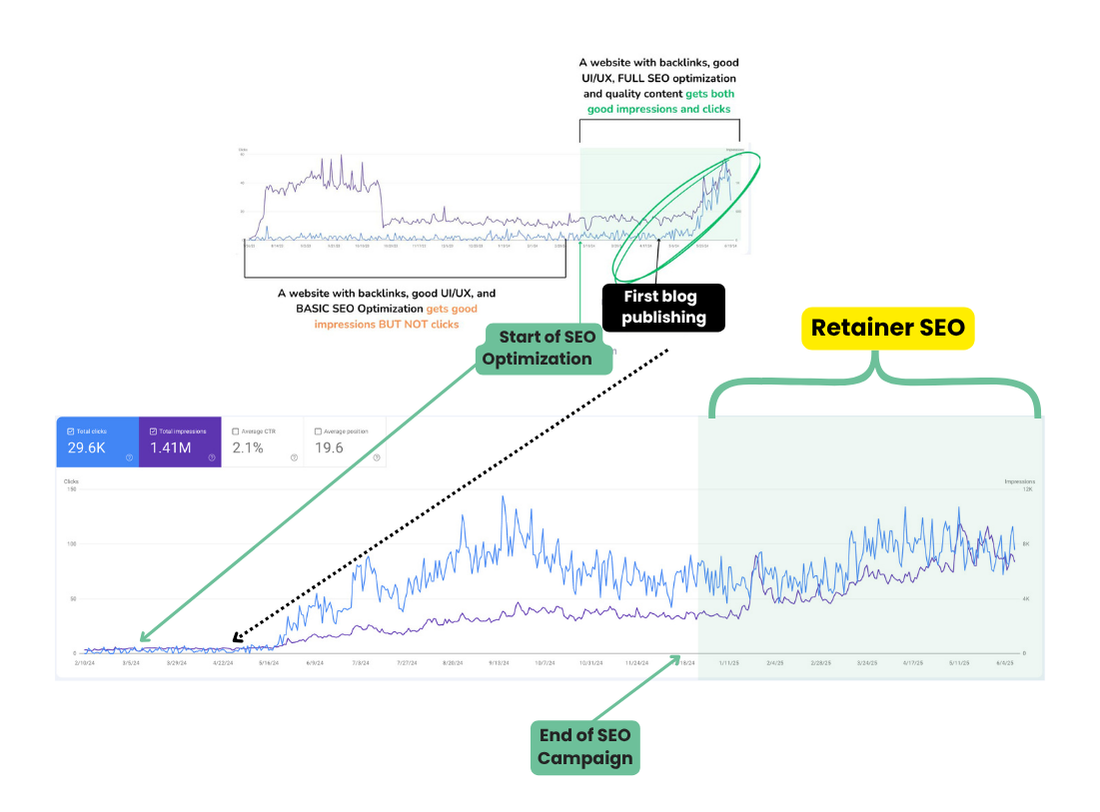
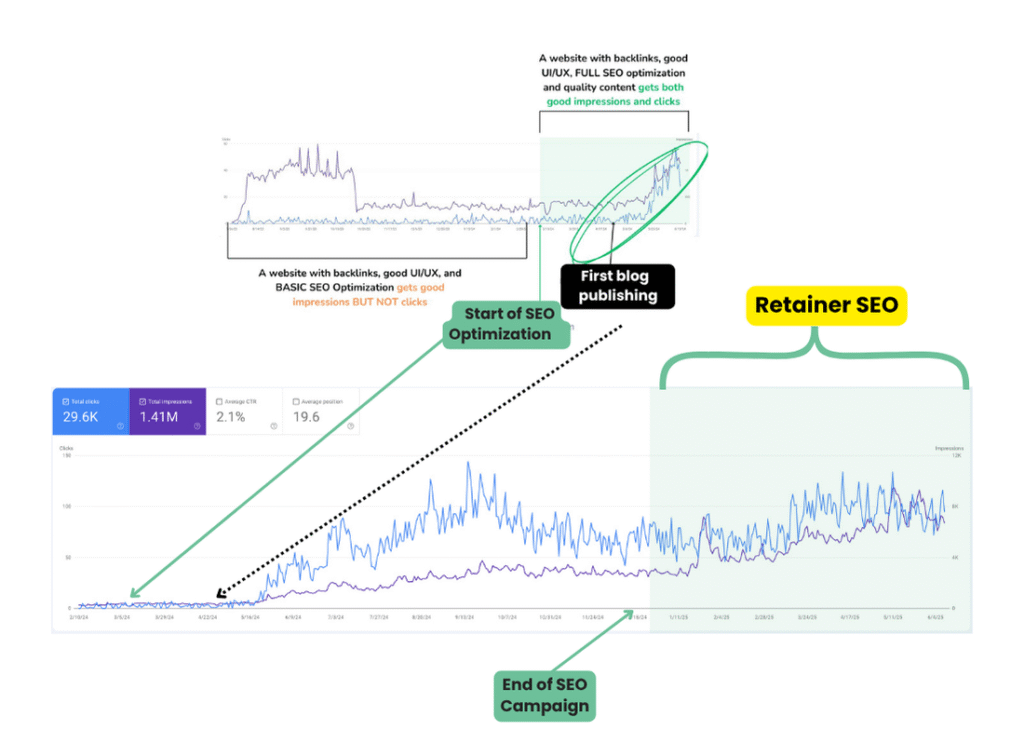
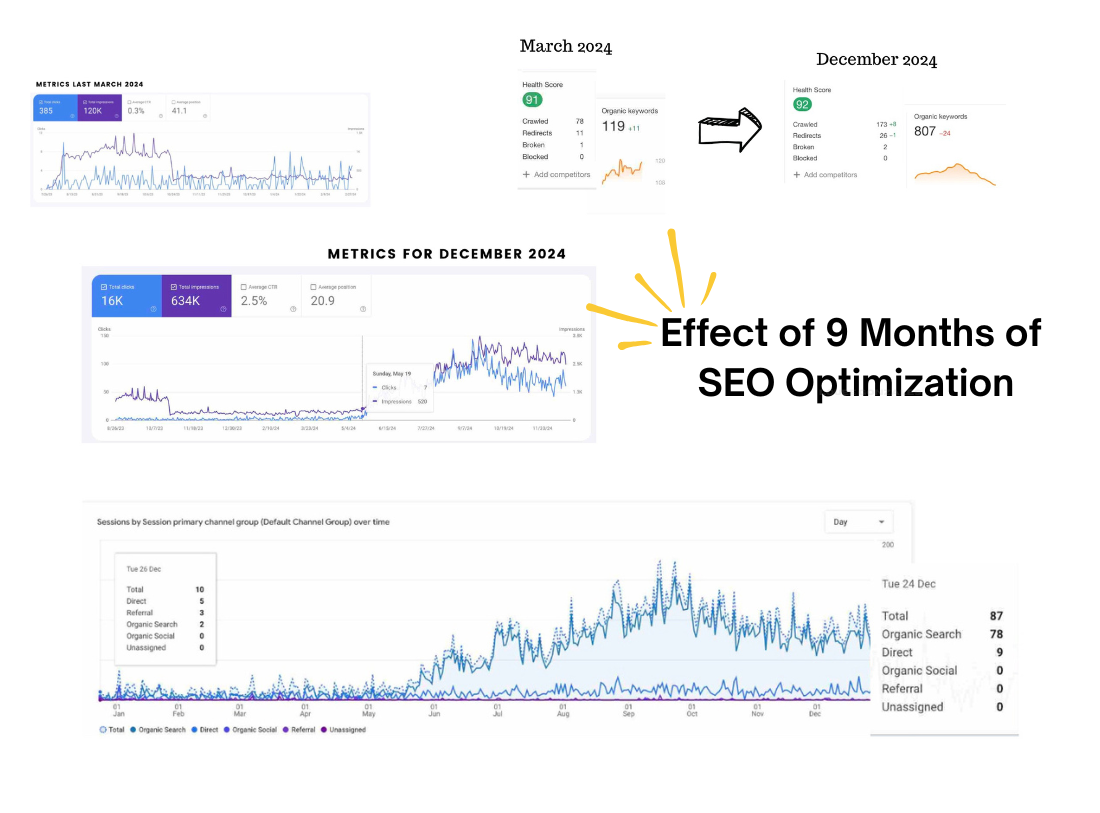
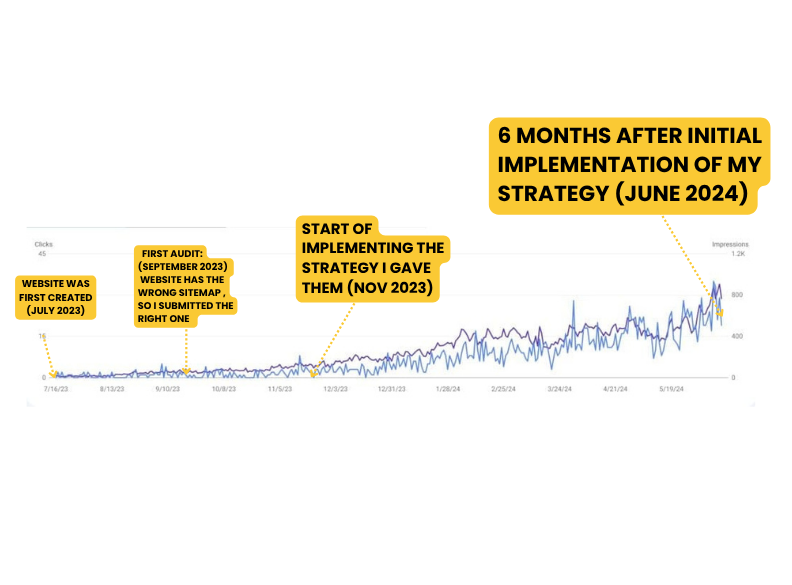
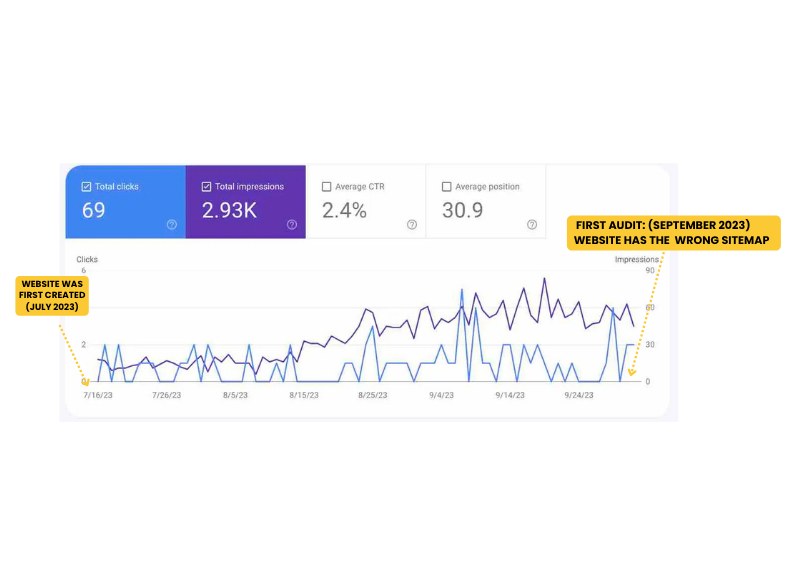
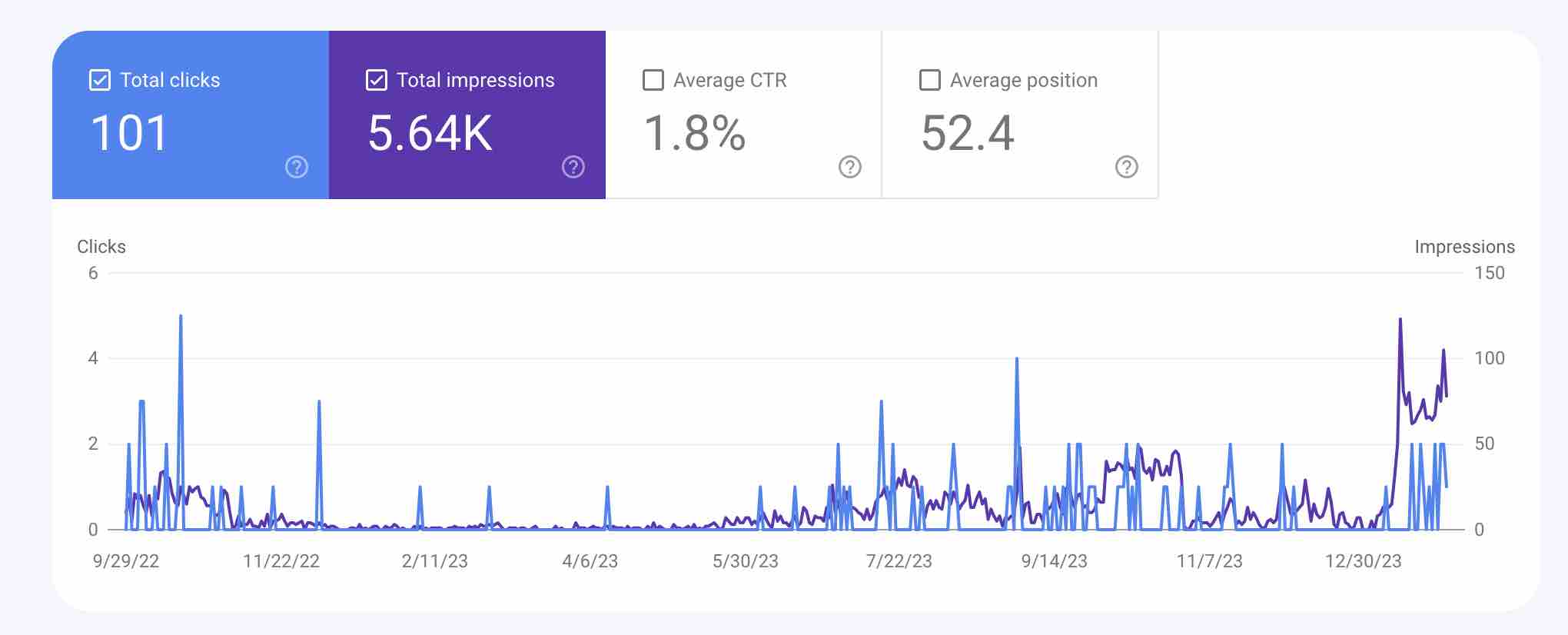
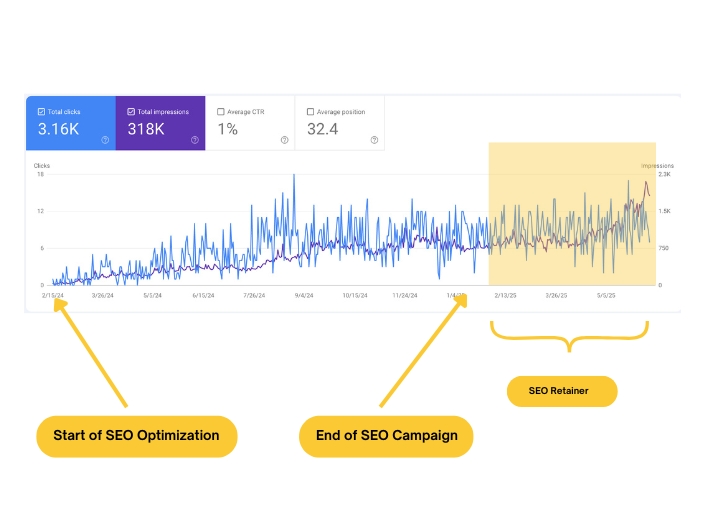
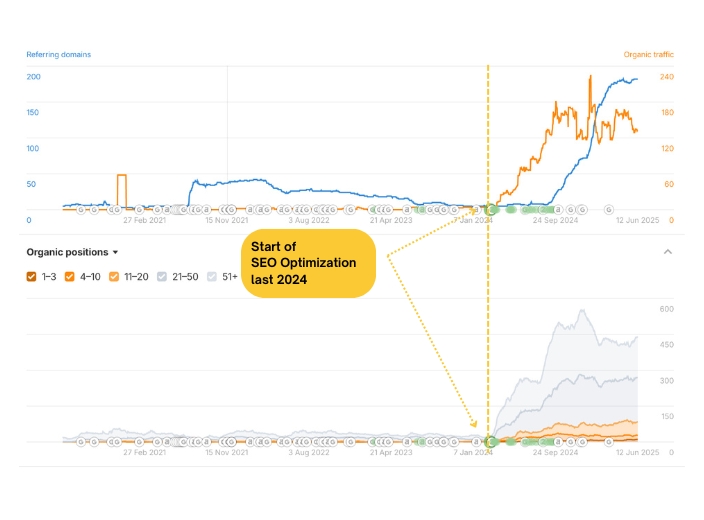
One of the most important things that you need to learn first about content writing is how to do on page SEO for your articles. In order to keep your website in the best shape and make your pages and content relevant for both users and search engine crawlers, you need to perform a number of optimizations.
At the end of the article, we have compiled an on-page SEO checklist that can guide you through this process and a PDF template that you can download as a sample.
>> Jump to Checklist and On-Page SEO Template
For good measure it’s always best to adhere to the Google Guidelines for SEO, but as it may sound super technical at first, here’s a breakdown of what Google wants from your website and content.
Related Reads:
Actionable Guide to On-Page SEO: Enhancing User Experience and Search Engine Rankings
SEO Internal Linking Best Practices for Beginners
On-Page SEO Examples of Implementation: Beginner’s Guide to On-Page SEO
Let us first talk about writing content.
Writing Content
Alright, so you have done your keyword research and picked the appropriate terms and strategy to get a good traffic volume and reflect your business and now you need to create content around them. That’s the easy part, and what’s the hard part?
Ranking on the first page.
In fact, studies show that most people don’t go beyond exploring the first 3 websites that pop up for any given search query. Think of yourself as the one putting in that query, would you open the 5th or 6th or the 8th link on a search page? Most likely not.
This is why it is crucial to be at the top.
In order to rank high, the first thing you need to do is analyse your competitors. Check your competition that is ranking for the keyword you are targeting. Read the content and find out where it is lacking.
Do you think that a certain thing should have been included in the content? Great! Put it in your content.
Answer questions that you feel are not being answered in your competitor’s post and make better content yourself. Make the content as engaging as possible. Use powerful sub-headings that answer queries answers.
This can also put you in one of the featured snippets on the first page, even if you are not in the first position for the desired query. More about this later on in the post.
Make Lengthy Content
You wish to write something about something? Make it informative and long!
Make the content as informative as possible. If you open most of the top results in a search engine, you will find out that most pages are well-written and well beyond the 1500 words mark, with some of the content being as long as 4000 words.
This goes on to show how much Google values lengthy content that can explain its topic in detail. Give as much detailed information as you can. People stay on your website for reading content that is truly valuable and unique. I
If you already know what your competitor’s content lacks in, you can easily fill in the gaps and make content that is better than your competitors.
Writing lengthy content also allows you to cover a lot of different topics on the same page. Google would rather want you to pack related topics into one page than make a different page for each.
Due to this, always avoid writing thin content that is not informative enough.
Google would prefer you to make one strong content rather than making multiple thin variations of the same topic divided into several pages.
Avoid Duplicate & Scraped Content
Duplicate content, as the name suggests, refers to content that is copied from another domain, or from another page within a single domain. Taking it a step further, ‘scraped’ content is content that is used by a person, without the permission or authorization of the owner/author, and publishing it under their own name.
While duplicating or copying content from elsewhere might not directly impose a penalty on you, it is highly discouraged. It takes out the credibility out of your website and in most cases, Google only shows one single result of the duplicated contents.
This is to avoid people navigating to the same content over and over again, without gaining any new information.
If you have multiple pages with the same content, use the rel=canonical tag to point the crawler to the original source of the content. This way it will know that it contains duplicated content from another page.
Cloaking
Cloaking is a practice of hiding content under the HTML part of your website, which is not visible to the human visitor but can be detected by a search engine.
This practice is often used by users to try to mislead the crawlers into detecting lengthier content.
The practice can be both good or bad, and Google ‘might’ rank you for it, if it enhances the user experience.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing has been a consistent part of on-page SEO and is considered one of the best SEO practices. However, in today’s times, keyword stuffing is nothing but one part of your strategy. You might have heard several people saying that you need to mention your keyword at least X times in your content.
True, mentioning your keyword in your content is important and it makes your content appear relevant to that keyword. Though, Google not only checks the density of the keyword that has appeared in your content, but also other key terms that are relatable to the keyword.
If these terms, known as LSI keywords, are present in your content and can be seen used in support of your original keyword, Google deems your content to be relevant and well-written.
There are no ‘X times’ you need to insert your keyword into your content. You may keep it to a good 2-3% of your content length as long as you are writing informative content. While writing, the use of LSI keywords can be a good indicator for crawlers that your topic is covering different aspects of the topic and is using relatable terms.
Auto-Generated Content
Let me just say that I’m not against those using AI writers. I’m just not advocating the use of an AI writer alone and not editing or fact-checking a piece before publishing.
The practice of auto-generating content through a program is often the lowest quality SEO practice one can perform. Auto-generated content is used for manipulating search engines and makes little sense to the readers. It is often robotic and is created by spinning and changing existing content by modifying synonyms.
This content can neither be quality-based nor reliable. It provides no value to the user as its unreadable in most cases. With machine learning growing, auto-generated content has been getting better and hard to detect but it’s still a practice that should not be too relied on.
But you know what, I also believe that auto-generated content can be useful as a guide if you have no idea how to start your article. The best way to use autogenerated content is just to use it as a jumpstart and insert a human touch into your pieces than just letting the AI write for you.
Create Specialized Content Based On Locations
So you are in a business that spans several locations or cities. When creating your website, it is important that you mention all your primary contact details on the right pages. Mostly, this information can be found in the header or footer section of your pages, especially on the “Contact Us” page.
The information must be displayed prominently and accurately to the user.
For offices at more than one location, you can create separate pages, uniquely describing the services at each different location. For example, for City Abc and City xyz, you can create separate pages, like domain.com/abc and domain.com/xyz.
Besides optimizing your content, there are several best SEO practices that you can perform to upscale your on-page SEO. These most typically deal with HTML tags that are responsible for showing your page data to the crawlers and the search engines.
Header Tag
Header tags are HTML tags that are used to define the headings on your page. These go from <h1> to <h6> in decreasing order of importance. The H1 tag is the main tag, which is used to describe the main heading of your page.
The H1 tag is usually derived from the title of the page. From H2 to H6, all are used to describe sub-headings on a page.
<h1> The Main Heading </h1>
<h2> Level 1 Sub-Heading </h2>
<h3> Level 2 Sub-Heading</h3>
<h3> Level 2 Sub-Heading </h3>
The header tags can be used to differentiate sub-sections of your page and are a great indicator for crawlers. These can divide your pages according to the importance and sub-headings of your topic.
The primary use of the header tag should be limited to discussing what the upcoming paragraph or media will be about. Other than this, it should not be used for buttons or phone numbers, or any such element.
While the main heading enclosed in H1 provides the topic of the page, the H2 sub-heading is more specific in what is going to be discussed, and with H3, we move into even more specific topics.
Title Tag
The Title tag is an HTML element that describes the title of your page. It is enclosed within the head tag and what you write in it appears as the title for your page in the browser as well as search engines.
<head>
<title>Your Page Heading</title>
</head>
Your title must be descriptive of the page content. The same titles for two pages from a single domain may arise confusion, which is why it is important to create a unique title. The title tag is what will show for your page in search results
This article for example, “How to do On-Page SEO | Template and Checklist” is the title of the page.
Similarly, the Title tag will appear when you share your link elsewhere, this goes the same if you’re sharing a blog post on another platform like this:
Title Tag Optimizations
- Significance: Your title is reflective of your page’s content and will be the first thing users read in SERPs. A good title can drive users to your website and make them read your content. Make your title informative and use modifiers as well as adjectives, such as “top”, and “best” to make your title look ‘powerful’.
- Keyword in Title: Also, make sure that your main keyword is included in the title. This can help both the search engines and users better understand the intent of your page. The closer your keyword is to the front, the more your chances are of getting a higher position and getting higher click rates.
Quick Tip: Try starting your title from your main keyword, as long as it does not look unnatural.
- Length Optimization: The length of your title should fall in the range of 50-60 characters, as most search engines only allow up to the first 60 characters to be displayed on the SERPs. Beyond that, your title will be cut off with an ellipsis “…”. However, it is not a concrete practice that you must always perform if your title provides valuable information.
- Branding: Everyone loves branding, and why not? Most people mention their own brand name at the beginning or at the end of the title. It creates awareness of the brand publishing the content and trustworthiness for recurring readers.
Meta Description
Similar to the Title tag, Meta description tag are HTML elements that describe the page content to the search engine and is shown in SERPs for the user. The meta description provides a short summary of your page and is mentioned below the title tag in a search result.
These are also enclosed within the head tag of your HTML document.
<head>
<meta name=”description” content=”summary of your page”/>
</head>
This meta description looks like this on the search page:
In the above image, Google automatically fetched a “description” of the content. This feature was rolled out last 2020, but as a good practice, you can set your own meta description just in case Google decides to use it, right?
In most cases, Google may put a more relevant description than the one already mentioned by you, from your page’s content. Nonetheless, you should still always provide a default meta description for each page.
- Optimize Description: The meta description should provide a quick summary of your key concept in it. Try to write something that engages the user and makes him think that you have the right solution for his/her search query.
You can also use your main keyword in the description for boosted results.
- Description Length: Your meta descriptions should be around 150-200 characters long for them to display on the SERP appropriately. Any more than that and it will be cut off.
URL Structure
URL is the short form for Uniform Resource Locator. URLs are addresses for HTML pages on the web. Just like title tags and meta descriptions, these URLs are shown in the browser and the search engine results pages.
The naming and formatting of this can highly affect your click rates. A well-formatted URL is easy to identify for users and also crucial for search engines in evaluating your pages.
Organizing Page Names
Search engines promote the use of unique URLs for each page of the website so that they can be displayed in the search results properly. However, it is also important to use clean URLs that can convey the topic to the reader, without visiting the URL. For example,
domain.com/clothing/mens-clothing
domain.com/pid?=7864
The first URL conveys not only more information to the user, but it is also easy to remember for most. It clarifies the information that is contained on the page and does not confuse the user. Keep in mind that user interaction is your primary motive.
Make it convenient for people to look up and search your URLs.
Avoid Nesting Under Wrong Folders
Another thing to make sure of is your pages are not nested under the wrong or irrelevant folders. The folder’s name is reflective of the type of pages under it. This also provides an indication to the search engine. Similarly, a news-based website may put its content in time-indicative folders, but it might not be appropriate for a blog to do so.
All in all, short URLs are preferred by both search engines and witness a better click rate from the users. This gets us to our next topic, URL length.
URL Length
Studies show that shorter URLs have better click-through rates than their longer counterparts. People seem to prefer URLs that are shorter and descriptive rather than the ones which are heavily nested. For example,
domain.com/food-items/bakery/cakes/blueberry-cake
OR
domain.com/bakery/blueberry-cake
In most cases, people will prefer the second one. And just like title tags and meta descriptions, if the URL is too long, it will be cut off in the SERP. Try to keep your URL short and descriptive enough to guide the user properly.
You can minimize length by including fewer words in the page title and removing any unnecessary subfolders. This will also make your URLs easier to copy and paste.
Placing Keywords in URL
When targeting a keyword, you can put it in the URL to boost the relevancy of the page. However, you need to make sure that you only put it in the URL, if it naturally fits in there. If you are going overboard and stuffing your URL with multiple keywords, the search engine might detect it.
This is the case when you have multiple folders that are named in relation to the page. If you have your page under various nested folders and they are optimized for your targeted keyword, your URL might appear to be keyword-stuffed.
This practice can make you appear manipulative and spammy. Your URL should look natural and as mentioned in the point above, try to keep your URL short to avoid this.
HTTPS Protocol
The “s” in “https” stands for secure. Google recommends that all websites run on a secure protocol i.e. HTTPS. To make sure that you are using the HTTPS protocol, you need to obtain an SSL certificate. These certificates are used for encrypting data.
These ensure that the data passed between the browser and web server remains private. For sites running on HTTP, Google Chrome displays a “not secure” sign causing the sites to appear untrustworthy and unreliable.
Additional Tips
- Whenever modifying or creating specific URLs for your page, try to avoid the usage of plus signs (+), spaces (%20), or underscores (_). Instead, use a hyphen character (-) for separating words in a URL.
- Always avoid having case-sensitive URLs. Always opt for a lowercase URL approach.
Internal Linking
A website’s crawlability highly depends on its internal linking structure. When you link to different pages under your own website, you ensure that the crawlers are able to find all your website’s pages. Thus, all your pages are crawled equally and it also helps users to better navigate through your website.
A great example of internal linking is how Wikipedia links different topics on one page.
Links that are required to be clicked, such as from a drop-down menu, are mostly hidden from search engine crawlers. If your internal pages are linked through this type of approach, your pages might never get indexed. Due to this, it is vital to have other ways to connect to the pages.
Anchor Text
With the use of Anchor text in HTML, you can link text to other pages. The following is an example of anchor text in HTML
<a href=http://www.domain.com/”></a> – Example: http://www.domain.com/
<a href=http://www.domain.com/” Title=”Keyword”>Keyword</a> – Example: Keyword
The anchor text indicates the type of content that is available on the destination page. It is an indication for search engines that if I link to another page with the anchor text “apple pie”, the targeted page will be about apple pie.
However, you need to make sure that you don’t go overboard with the practice. Overuse of internal links using the same keyword anchor can appear as if you are trying to manipulate the rankings.
Hence, it’s better if you make anchor text fit naturally in your content.
Link Volume
Another thing to take care of when using anchor texts is the number of links on a given page. Having too many links on your page will not directly impose a penalty on you, but will affect how Google evaluates and ranks your pages.
The more links that appear on a page, the lesser authority they pass to their targeted pages. A page can have only a limited amount of authority, and if you end up linking too much out of it, each link will get lesser authority passed.
Moreover, aside from passing authority, links also serve as a way for the user to navigate better through the website. While you optimize your links for search engines, you will also get the added benefit of making better navigation for users.
Use links that are helpful and provide quality to the search engine as well as the user. Spamming too many links in your content will take the readability value out of it.
Redirecting Pages
Renaming or removing pages is a common occurrence, but when you do it, it is important that you update all links pointing toward that page. At the very least, you need to redirect all the URLs to the new location. However, it is highly advised that you update all internal links so that the users and crawlers do not have to go through redirects to arrive at the targeted page.
Moreover, having too many redirects may affect your on-page SEO. As stated by Google, you should avoid chaining redirects, ideally no more than 3 and fewer than 5.
Image Optimization
Images occupy the most space in a site and are the culprits of most slow web pages. The best way through which you can solve it by compressing your images. There are various solutions when it comes to image compression, you can try testing options like “Save for Web” in Photoshop, image sizing software or compression tools, such as TinyPNG or Canva.
Knowing which image format can exhibit your image intent best is also important.
- GIF – To be used when you need to use an animated image
- JPEG – When you don’t have to preserve high image resolution
- PNG – When you have to preserve high image resolution
- PNG-24 – When your image has a lot of colors
- PNG-8 – When your image does not have a lot of colors
If you own an e-commerce website, your thumbnails might slow down your page’s loading speed. Most people leave your page within 3 seconds if it’s not loaded properly. Due to this, it is essential that you compress your images and optimize your images.
Alt Text
Alt text or alternative text describes the image to the visually impaired through screen readers. It is important to have alt text descriptions for an image so that a visually impaired person can understand what the picture depicts on your web page.
Search engine crawlers also use alt text to better understand the purpose of your image, which provides an additional benefit of expressing better image context to Google. However, you need to make sure that your alt text does not read robotically. It should be natural, just like your content. For example,
<img src=”weddingbride.jpg” alt=”A bride moving towards her wedding stage”>
Improving Readability of your Site
Your site may contain the best-written content, but without proper formatting, your audience might never be able to enjoy it! It is important to follow some principles that boost the readability of the overall site. These are as follows:
- Headings: Break up your content with helpful headings. These can help the users navigate through all the sections of the page, especially when the user is looking to read a particular section rather than the whole content.
- Bullet Points: Bullet points provide a great way of providing quick and accurate information to the users.
- Text size & color: Avoid fonts that look too big or too tiny. Google recommends that you use a 16-point font to make your text readable, even on mobile. The text color should complement the page’s background to promote readability.
- Paragraph Breaks: Avoid writing walls of text without any break. People prefer reading shorter sentences and a big piece of content might get totally ignored, if not divided in the right way. Shorter paragraphs encourage visitors to stay and read more of your content.
- Supporting Media: Always try using appropriate media, such as videos or images that complement your content or can help describe a related topic.
- Bold & Italics: Make use of bold and italics wherever applicable to put emphasis on particular things. Correct usage of these formatting options can help you highlight key points of your content.
By better formatting your site and its content, you provide a better user experience to the readers. Moreover, it can also boost your page’s ability to show in feature snippets or better known as “position 0”
Featured Snippets
A featured snippet is the unofficial “position 0” which appears at the top of a SERP. There is no special way or code that you can insert for your page to show in this place.
What you can do is structure your content to better answer a query intent and you will eventually be there. This is what a featured snippet looks like (as shown in Google):
For any given query, if you are providing a suitable result in a well-formatted manner, your chances of getting featured in a snippet increase. For example, for a query searching to “learn SEO”, you can create a bullet list of points and if Google deems it good, you might have your full list of points featured in the snippet.
On Page SEO Checklist and Final Words
By following the above-mentioned on-page SEO checklist, you can create a website that is well-optimized for both users and search engines. Not only will it affect your search engine rankings and crawlability, but also enhance the experience of users when they visit your website.
Here’s the checklist to guide you when optimizing every post/page on your website:
This may look tedious but we’ll have future posts that will guide you on how to optimize for these with or without plugins!
For now, you can download the sample template for on-page SEO.
Download the above On Page SEO Template for your future reference
Remember, that the practice of on-page SEO is an ongoing process. The process has constantly evolved with the introduction of various algorithm updates in the past and will keep growing in the future.